Case Study 1
Auto Parts Manufacturing - Streamlining Production with Robotic Welding and Assembly (Automotive Industry)
Challenges
Traditional auto parts manufacturing relies on manual welding and assembly processes, leading to inconsistencies, potential for human error, and dependence on skilled labor. Manufacturing companies struggle to meet high production volumes and ensure consistent quality across a wide range of parts.

Solution
Auto parts manufacturers can implement robotic welding and assembly lines. Industrial robots equipped with welding torches and grippers can automate tasks like welding car frames, attaching components, and assembling complex parts. These robots can be programmed for precise movements and high repeatability, ensuring consistent quality.
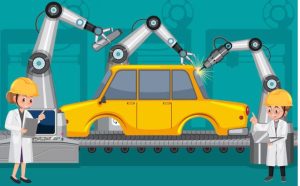
Benefits
Increased production volume and faster turnaround times with automated welding and assembly processes.

Improved product quality and consistency due to precise robot movements and repeatability.

Reduced reliance on skilled labor for manual welding and assembly tasks.

Enhanced safety by minimizing human exposure to welding hazards and repetitive motions.
Case Study 2
Electronics Manufacturing - Implementing Smart Factory for Real-Time Monitoring and Data-Driven Decisions (Electronics Industry)
Challenge
Traditional electronics manufacturing often lacks real-time production data and relies on manual quality checks. Manufacturing companies struggle to identify bottlenecks, optimize production processes, and ensure consistent product quality.

Solution
Electronics manufacturers can implement a smart factory concept. Production lines can be equipped with sensors that monitor machine performance, track component placement, and measure product quality parameters. This real-time data is aggregated and analyzed by a central platform for overall production visibility. Data-driven insights can then be used to identify bottlenecks, adjust production parameters, and optimize quality control processes.

Benefits
Improved production efficiency through real-time monitoring and identification of bottlenecks in the manufacturing process.

Enhanced quality control with data-driven insights and automated defect detection systems.

Data-driven decision making for optimizing production processes, resource allocation, and preventive maintenance.

Increased flexibility and adaptability to production changes based on real-time data analysis.
Case Study 3
Food Manufacturing - Optimizing Production Lines with Automated Packaging and Inventory Management (Food & Beverage Industry)
Challenge
Traditional food manufacturing relies on manual packaging processes and basic inventory management systems. Manufacturing companies struggle to ensure consistent packaging quality, minimize waste, and optimize inventory levels to prevent stockouts or overstocking.

Solution
Food manufacturers can implement automated packaging systems. These systems utilize robotic arms or conveyor belts with integrated vision systems for accurate filling, sealing, and labeling of food products. Additionally, smart inventory management systems can be implemented with real-time monitoring of raw materials and finished goods. Production planning can be adjusted based on inventory levels and sales forecasts to minimize waste and ensure product availability.
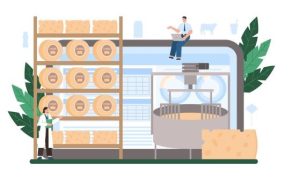
Benefits
Increased packaging efficiency and speed with automated systems.
Improved packaging quality and consistency through automation and vision inspection systems.

Reduced food waste due to overfilling or inaccurate portion control during packaging.

Optimized inventory management with real-time data on raw materials and finished products.
These cases showcase how automation technology can benefit manufacturing companies across different industries. By implementing robotic solutions, smart factory concepts, and automated packaging systems, manufacturing companies can achieve higher production volumes, improve product quality and consistency, optimize production processes, and minimize waste.
